Introduction
Photosynthesis is a fundamental process that sustains life on Earth. Through this process, plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, using carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen.
In experimental settings, scientists often use various techniques and substances to better understand the mechanisms of photosynthesis. One such substance frequently employed is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3).

This article delves into the reasons why sodium bicarbonate is an essential component in photosynthesis experiments.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesis
Before exploring the function of sodium bicarbonate, it is crucial to understand the significance of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis. The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ .
Carbon dioxide serves as the source of carbon atoms for the synthesis of glucose. During the Calvin cycle, which is the light – independent stage of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into organic compounds.
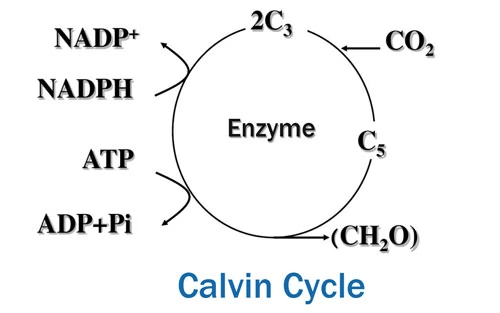
In natural environments, plants obtain carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, where its concentration is approximately 0.04% (400 ppm). However, in experimental conditions, especially those involving isolated plant parts or aquatic photosynthetic organisms, ensuring an adequate supply of carbon dioxide can be challenging.
Sodium Bicarbonate as a Source of Carbon Dioxide
Sodium bicarbonate is used in photosynthesis experiments primarily because it can act as a source of carbon dioxide. When sodium bicarbonate is dissolved in water, it undergoes a chemical dissociation:
NaHCO3(s)= Na+(aq)+ HCO3-(aq).
The bicarbonate ion ( HCO3-) can further react with water and release carbon dioxide:
HCO3- + H2O ↔ H2CO3 + OH-
H2CO3=H2O+ CO2↑.
(For more explanation on sodium bicarbonate, please read “sodium bicarbonate reaction with water“.)

This process provides a continuous supply of carbon dioxide in the experimental system. For example, in an experiment using aquatic plants like Elodea, placing the plant in a solution containing sodium bicarbonate allows the plant to access carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. As the plant uses up carbon dioxide in the surrounding water, more is released from the dissociation of sodium bicarbonate, maintaining a relatively stable concentration of carbon dioxide available for the photosynthetic reactions.
Controlling Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Another advantage of using sodium bicarbonate in photosynthesis experiments is the ability to control the concentration of carbon dioxide. By varying the amount of sodium bicarbonate added to the experimental solution, researchers can manipulate the availability of carbon dioxide for the photosynthetic organisms. This is crucial for studying the impact of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis.
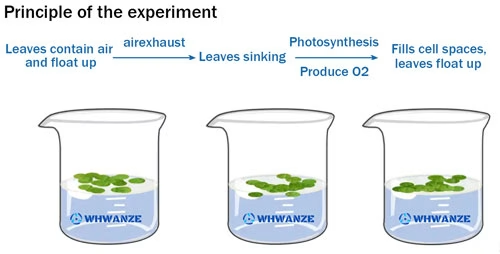
For instance, if a scientist wants to investigate how different levels of carbon dioxide affect the growth and photosynthetic efficiency of a particular plant species, they can set up multiple experimental groups with different concentrations of sodium bicarbonate solutions. A low – concentration sodium bicarbonate solution will provide a relatively low level of carbon dioxide, while a high – concentration solution will supply more carbon dioxide. By measuring parameters such as oxygen production, glucose synthesis, or the rate of carbon fixation in each group, the researcher can determine the relationship between carbon dioxide concentration and the photosynthetic process.
Comparing with Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
In natural conditions, plants are exposed to the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere. However, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can be limiting for photosynthesis in some cases, especially for plants growing in crowded or shaded environments. In experimental settings, using sodium bicarbonate allows researchers to simulate different carbon dioxide availability scenarios, including conditions where the carbon dioxide concentration is higher than that in the atmosphere.

This is beneficial for understanding the potential of plants to increase their photosynthetic rates when provided with more carbon dioxide. For example, in studies related to improving crop yields, scientists can use sodium bicarbonate – based experiments to determine if supplementing carbon dioxide can enhance the growth and productivity of agricultural plants. By comparing the photosynthetic performance of plants in the presence of sodium bicarbonate – derived carbon dioxide with their performance under normal atmospheric conditions, valuable insights can be gained into the factors that limit photosynthesis and how they can be overcome.
Impact on the Rate of Photosynthesis
The addition of sodium bicarbonate to a photosynthesis experiment has a direct impact on the rate of photosynthesis. As the concentration of available carbon dioxide increases due to the dissociation of sodium bicarbonate, the rate of carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle also increases. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the production of glucose and the release of oxygen.

Several studies have demonstrated this relationship. For example, in an experiment with spinach leaves, discs were floated in sodium bicarbonate solutions of different concentrations under light. The number of leaf discs that floated to the surface (an indication of oxygen production) was counted over time. It was found that as the concentration of sodium bicarbonate increased, more leaf discs floated, indicating a higher rate of photosynthesis. This is because the increased availability of carbon dioxide provided more substrate for the photosynthetic reactions, enabling the plants to produce more oxygen and organic compounds.
Considerations in Using Sodium Bicarbonate
While sodium bicarbonate is a valuable tool in photosynthesis experiments, there are some considerations to keep in mind.
- Firstly, the concentration of sodium bicarbonate should be carefully selected. If the concentration is too high, it can lead to osmotic stress on the photosynthetic organisms. The high concentration of ions in the solution can disrupt the balance of water and solutes within the cells, potentially affecting their normal physiological functions.
- Secondly, the pH of the solution can be affected by the presence of sodium bicarbonate. As the bicarbonate ion dissociates, it can influence the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution. This change in pH can impact the activity of enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Therefore, in some experiments, it may be necessary to buffer the solution to maintain a stable pH and ensure that the observed effects on photosynthesis are due to the availability of carbon dioxide rather than changes in pH.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium bicarbonate plays a vital role in photosynthesis experiments. It serves as a reliable source of carbon dioxide, allowing researchers to control and manipulate the availability of this essential substrate for photosynthesis. By using sodium bicarbonate, scientists can study the impact of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis, compare different carbon dioxide availability scenarios with natural atmospheric conditions, and gain a better understanding of the factors that limit and enhance photosynthesis. However, proper consideration must be given to the concentration of sodium bicarbonate and its potential effects on osmotic balance and pH to ensure accurate and meaningful experimental results. Overall, the use of sodium bicarbonate has significantly contributed to our knowledge of the complex process of photosynthesis and its underlying mechanisms.
Expand reading:

