I. Introduction
Sodium fluoride (NaF) is a chemical compound that has a wide range of applications and implications in various fields. From dental care to industrial processes, sodium fluoride plays a significant role. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of what sodium fluoride is, its properties, production methods, applications, and potential health and environmental impacts.
II. Chemical Properties of Sodium Fluoride
A. Chemical Formula and Structure
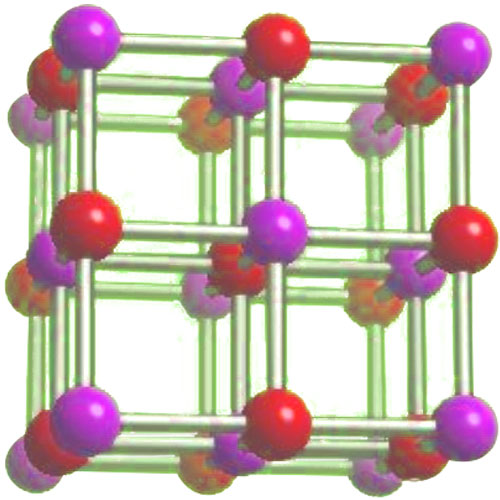
Sodium fluoride has the chemical formula NaF. It consists of one sodium ion (Na+) and one fluoride ion (F-). The sodium ion is positively charged, while the fluoride ion is negatively charged. The ionic bond between these two ions gives sodium fluoride its stability. The sodium fluoride is ionic and supports special properties due to its structure ( For details, please check “is sodium fluoride ionic or covalent“).
B. Physical Properties
- Appearance: Sodium fluoride is a white crystalline solid.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, forming a clear solution.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Sodium fluoride has a melting point of 993°C and a boiling point of 1704°C.
- Density: The density of sodium fluoride is approximately 2.558 g/cm³.
C. Chemical Reactivity
- Reaction with Acids: Sodium fluoride reacts with acids to form hydrofluoric acid (HF) and the corresponding salt. For example, when it reacts with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), it forms hydrofluoric acid and sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄).
- Reaction with Bases: It can also react with bases. However, the reactions are less common compared to its reactions with acids.
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions: Sodium fluoride is not typically involved in oxidation-reduction reactions.
III. Production Methods of Sodium Fluoride
A. Fluorspar and Sodium Hydroxide Reaction
One of the common methods of producing sodium fluoride is by reacting fluorspar (calcium fluoride, CaF₂) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The reaction produces calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) and sodium fluoride.
CaF₂ + 2NaOH → Ca(OH)₂ + 2NaF
B. Sodium Silicofluoride Hydrolysis
Sodium silicofluoride (Na₂SiF₆) can be hydrolyzed to produce sodium fluoride. This method is often used in industrial settings.
Na₂SiF₆ + 4H₂O → 6HF + SiO₂ + 2NaF
C. Neutralization Reaction
Sodium fluoride can also be produced by neutralizing hydrofluoric acid with sodium hydroxide.
HF + NaOH → NaF + H₂O
IV. Applications of Sodium Fluoride
Sodium fluoride is widely used in many fields, please check “Sodium fluoride uses” for detailed explanations.
V. Health Effects of Sodium Fluoride
A. Dental Health Benefits
- Strengthening Enamel
- Reducing Cavities
B. Potential Risks
- Fluorosis
- Skeletal Fluorosis
Long-term exposure to high levels of fluoride can also lead to skeletal fluorosis, a condition that affects the bones. Symptoms of skeletal fluorosis include joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In severe cases, it can lead to crippling deformities.
- Other Health Concerns
Some studies have suggested that excessive fluoride intake may be associated with other health problems, such as reduced IQ in children, increased risk of cancer, and thyroid disorders. However, the evidence for these associations is still controversial and more research is needed.
VI. Environmental Impact of Sodium Fluoride
A. Water Pollution
Release of sodium fluoride into the environment can lead to water pollution. High levels of fluoride in water can be harmful to aquatic life and can also affect the quality of drinking water. Industries that use sodium fluoride in their processes must take measures to prevent the release of fluoride into water sources.
B. Soil Contamination
Sodium fluoride can also contaminate soil. This can occur through industrial emissions, agricultural applications, and improper disposal of fluoride-containing products. Soil contamination with fluoride can affect plant growth and can also lead to the accumulation of fluoride in the food chain.
C. Air Pollution
Some industrial processes that involve sodium fluoride can release fluoride gases into the air, contributing to air pollution. These gases can be harmful to human health and can also damage plants and animals.
VII. Regulation and Safety Measures
A. Drinking Water Standards
Many countries have established standards for the maximum allowable concentration of fluoride in drinking water. These standards are designed to ensure that people receive an appropriate amount of fluoride for dental health benefits while minimizing the risk of fluorosis and other health problems.
B. Labeling Requirements
Products that contain sodium fluoride, such as toothpaste and mouthwashes, are required to have clear labeling indicating the presence of fluoride and providing information on its potential health effects. This helps consumers make informed decisions about the use of these products.
C. Industrial Safety Measures
Industries that use sodium fluoride must follow strict safety measures to prevent the release of fluoride into the environment and protect the health of workers. This includes proper handling, storage, and disposal of sodium fluoride and the implementation of pollution control measures.
VIII. Conclusion
Sodium fluoride is a chemical compound with a wide range of applications and implications. While it has significant benefits for dental health when made into toothpaste grade sodium fluoride. And it is used in various industrial processes, it also poses potential risks to human health and the environment if not used properly. Understanding the properties, production methods, applications, and health and environmental impacts of sodium fluoride is essential for making informed decisions about its use. By implementing proper regulation and safety measures, we can ensure that sodium fluoride is used in a way that maximizes its benefits while minimizing its risks.

