Sodium hexametaphosphate, with the chemical formula Na6O18P6, is an inorganic compound and a type of sodium metaphosphate polymer.
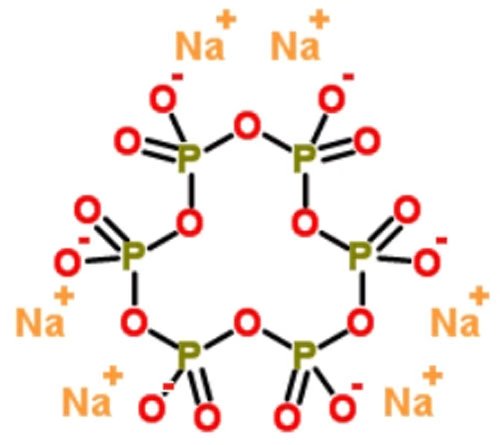
It is also known by several other names, including “polyvinylidene sodium,” “sodium multiple metaphosphate,” “sodium metaphosphate vitreous body,” and “Graham salt.” To know more about its explanation, please read “what is sodium hexametaphosphate”.
We have introduced most of sodium hexametaphosphate uses in previous blogs, and here we’d explain its usage in paint.
Functions of Sodium Hexametaphosphate in Paint
Dispersing Agent
In the paint industry, achieving a homogeneous dispersion of pigments is of utmost importance. Pigments are the coloring substances in paint, and their even distribution directly affects the color consistency, hiding power, and overall appearance of the paint film. Sodium hexametaphosphate serves as an excellent dispersing agent in paint formulations.

Sodium hexametaphosphate works to prevent pigment aggregation through several mechanisms.
First, it adsorbs onto the surface of pigment particles. The phosphate groups in sodium hexametaphosphate interact with the surface of the pigment particles, creating a layer around them. This adsorbed layer changes the surface properties of the pigment particles.
Moreover, the adsorbed layer of sodium hexametaphosphate also provides a steric hindrance effect. So, it can make the paint to have a more uniform color, better hiding power, and enhanced stability during storage.
Anti flocculation Agent
When pigment particles flocculate, the paint may be difficult to be applied evenly, evenmore, it may cause a reduction in the color strength and hiding power of the paint.

In a paint system with potential flocculation causing factors, the electrostatic repulsion and steric hindrance provided by the adsorbed sodium hexametaphosphate prevent the pigment particles from aggregating into flocs.
In this way, sodium hexametaphosphate helps to keep the pigment particles in a well – dispersed state, ensuring that the paint has consistent application properties, color performance, and durability over time.
Water softening Agent
In many paint application scenarios, especially for water based paints, the quality of the water used in the paint formulation can have a significant impact on the paint’s performance. Sodium hexametaphosphate can soften water by effectively remove calcium and magnesium ions.

The paint using soften water has better stability, improved flow properties during application, and enhanced adhesion to the substrate. The paint film formed also has better physical and chemical properties, such as improved resistance to water – related degradation and better color retention over time.
Advantages of Using Sodium Hexametaphosphate in Paint
Enhanced Color Development
One of the most noticeable advantages of using sodium hexametaphosphate in paint is its contribution to enhanced color development. As an effective dispersing agent, it plays a crucial role in ensuring that pigments are evenly distributed throughout the paint matrix.
Sodium hexametaphosphate helps to achieve a more uniform pigment dispersion. This results in a paint finish that has a higher color saturation, with brighter and more intense hues.

In large scale painting projects, where a consistent color across a large surface area is desired. Sodium hexametaphosphate reduces the likelihood of color blotches or streaks, providing a more professional and visually appealing finish.
Improved Storage Stability
Paint manufacturers and users alike value the improved storage stability that sodium hexametaphosphate brings to paint formulations.
Sodium hexametaphosphate acts as a stabilizer to prevent pigment settling and aggregation, keeps the pigment particles in a dispersed state.

This means that during long term storage, the paint can remain homogeneous, with the pigments evenly suspended in the liquid medium.
So, it ensures that the paint can be used as needed, without the need for additional processing or quality control measures to correct pigment related issues. This not only saves time and resources but also improves the overall efficiency of the painting process.
Better Film forming Properties
The addition of sodium hexametaphosphate to paint has a positive impact on the film – forming properties of the paint. A well – formed paint film is essential for providing protection, durability, and an attractive appearance to the painted surface.
For example, in a marine paint application, where the painted surface is exposed to harsh environmental conditions such as saltwater, moisture, and UV radiation, a paint with good film forming properties due to the presence of sodium hexametaphosphate can prevent corrosion of the metal substrate and extending the lifespan of the marine structure.

In decorative paint applications, such as on furniture or interior walls, a paint with improved film forming properties give the surface a more luxurious and professional look. Additionally, the improved durability of the paint film means that it can withstand normal wear and tear, maintaining its appearance for a longer period.
Application Scenarios and Dosage Considerations
Different Types of Paints
Sodium hexametaphosphate finds diverse applications in various types of paints, each with unique performance requirements and responses to its addition.
Water based Latex Paints:
Sodium hexametaphosphate helps to break down the pigment aggregates. So, it can make the paint with a consistent color, high hiding power, and good color stability. And it allows for a smooth and even application on objects.

Solvent based (Oily) Paints:
The application of sodium hexametaphosphate is more limited because of its insolubility in organic solvents. However, in some cases where there are water soluble contaminants or metal ions present in the solvent-based system that could affect the paint quality, sodium hexametaphosphate can be used in a pre-treatment step.
For instance, if the solvent used contains trace amounts of water with dissolved calcium ions, adding a small amount of sodium hexametaphosphate can complex with the calcium ions, removing them from the system and preventing potential issues like paint gelling or the formation of insoluble precipitates during storage or application.

Powder Coating:
Powder coatings are dry, free-flowing powders that are electrostatically applied and then cured to form a protective and decorative film. The sodium hexametaphosphate can be used in the pre-treatment of the substrate before powder coating application.
In the process of metal surface pre-treatment for powder coating, if the water used in the cleaning or etching steps is hard water, sodium hexametaphosphate can be added to soften the water. It helps to prevent the formation of scale or deposits on the metal surface, which could interfere with the adhesion of the powder coating.

Dosage Determination
Determining the appropriate dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate in paint is a complex process that depends on several factors.
Paint Formulation:
The overall composition of the paint, including the type and amount of binder, solvents, and other additives, can influence the optimal dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate. For example, in a paint with a high-solids content, more sodium hexametaphosphate may be required to effectively disperse the pigments. The binder in the paint can also interact with the sodium hexametaphosphate. Some binders may have a natural tendency to cause pigment aggregation, and in such cases, a higher dosage of the dispersing agent may be needed to counteract this effect. Additionally, if the paint contains other additives that affect the surface charge or rheology of the system, the dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate may need to be adjusted accordingly.

Pigment Type and Concentration:
Different pigments have varying surface properties and degrees of aggregation tendency. For instance, organic pigments often have a more complex surface chemistry compared to inorganic pigments and may require a higher dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate for proper dispersion. The concentration of the pigment in the paint also matters. Higher pigment concentrations mean there are more pigment particles to be dispersed, so a larger amount of sodium hexametaphosphate may be necessary to ensure that each particle is effectively separated and stabilized. For example, in a high-color -strength paint where a large amount of a particular pigment is used to achieve a vivid color, more sodium hexametaphosphate may be added to prevent the pigment from clumping together.

Desired Paint Properties:
The final properties that the paint is intended to possess also play a significant role in determining the dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate. If the goal is to achieve maximum color development and hiding power, a sufficient amount of the dispersing agent should be added to ensure optimal pigment dispersion. On the other hand, if the focus is on improving the storage stability of the paint over a long period, the dosage may be adjusted to prevent pigment settling and aggregation during storage. For paints with specific application requirements, such as those used in high – performance industrial coatings where a smooth and uniform film – forming is crucial, the dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate may be optimized to enhance the flow and leveling properties of the paint.

Typically, the dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate in paint formulations ranges from 0.1% to 5% by weight of the pigment. However, this is a very general range, and in actual paint production, extensive testing and optimization are carried out to determine the exact dosage that will best meet the specific requirements of each paint product.
Comparison with Other Additives in Paint
When comparing sodium hexametaphosphate with other similar additives in terms of performance and cost – effectiveness, several factors need to be considered.
Performance Comparison:
Dispersion Efficiency:
Sodium hexametaphosphate is highly effective in dispersing inorganic pigments, especially those with relatively simple surface chemistries. For example, it works very well with titanium dioxide, which is a common white pigment in paint. However, polyacrylic acid – based dispersants often outperform sodium hexametaphosphate when it comes to dispersing organic pigments. Organic pigments have more complex surface structures, and the long – chain steric – stabilizing action of polyacrylic acid – based dispersants is better suited to keep them well – dispersed.

Water – softening Ability:
Among the additives mentioned, sodium hexametaphosphate and sodium tripolyphosphate ( to know sodium tripolyphosphate please read “What is sodium tripolyphosphate“) have strong water – softening capabilities due to their high affinity for calcium and magnesium ions. Organic surfactants generally do not have significant water – softening properties. In paint systems where water quality is a concern, such as in water – based paints, sodium hexametaphosphate and sodium tripolyphosphate are more suitable choices.
Anti – flocculation Performance:
Sodium hexametaphosphate provides good anti – flocculation properties by creating electrostatic repulsion and steric hindrance. Anionic surfactants can also be very effective in preventing flocculation, especially in systems where the pigment – particle surface charge can be easily manipulated. However, non – ionic surfactants may not be as effective in preventing flocculation in some cases, especially when the paint system is exposed to changes in pH or electrolyte concentration.

Cost – effectiveness Comparison:
Cost per Unit:
Sodium hexametaphosphate is relatively inexpensive compared to some high – performance polymeric dispersants like polyacrylic acid – based dispersants. The cost of production of sodium hexametaphosphate is relatively low due to its simple chemical structure and common raw materials. Organic surfactants can vary widely in cost, with some specialty surfactants being quite expensive, while more common ones may be in a similar price range to sodium hexametaphosphate.

Dosage Requirements:
The dosage of sodium hexametaphosphate required in paint formulations is typically in the range of 0.1% – 5% by weight of the pigment. Polyacrylic acid – based dispersants may require a lower dosage in some cases, especially when dealing with difficult – to – disperse pigments. However, considering the cost per unit, sodium hexametaphosphate can still be a cost – effective option, especially for paints where the pigment – dispersion requirements are not extremely demanding. In large – scale paint production, the cost savings from using a relatively inexpensive additive like sodium hexametaphosphate can be significant, even if the dosage is slightly higher compared to some other additives.

In conclusion, while there are several additives in the market with similar functions to sodium hexametaphosphate, the choice of additive depends on the specific requirements of the paint formulation, the type of pigments used, and the cost – effectiveness considerations of the paint manufacturer. Sodium hexametaphosphate remains a popular choice in many paint applications due to its good overall performance and relatively low cost.
Future Trends and Research Directions
New Applications and Research in the Field
As the paint industry continues to evolve, there is a growing interest in exploring new applications and research directions for sodium hexametaphosphate.
Smart or self-healing paints
Smart paints are designed to respond to environmental stimuli, such as temperature, humidity, or mechanical stress. Sodium hexametaphosphate could potentially play a role in the formulation of these paints by interacting with other components to create a responsive system. For example, it could be used to enhance the sensitivity of the paint to certain environmental factors through its metal – ion complexing ability. By complexing with metal ions in the paint matrix, it might trigger changes in the paint’s properties, such as color or conductivity, in response to external stimuli.

Nanocomposite paints
Sodium hexametaphosphate can help to evenly distribute these nanoparticles in the paint, preventing their aggregation and ensuring that the enhanced properties are uniformly distributed throughout the paint film. This could lead to the development of high – performance paints with improved scratch resistance, corrosion protection, and antibacterial properties.
Sustainable paints
In bio-based paints, which use renewable raw materials, sodium hexametaphosphate could help to stabilize the formulation and improve the dispersion of natural pigments or fillers. This could contribute to the development of more sustainable paint products that are both eco – friendly and have excellent performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Sodium hexametaphosphate, with its unique physical and chemical properties, plays a multifaceted role in the paint industry.
Looking ahead, the future of sodium hexametaphosphate in the paint industry appears promising. As research continues, new applications are likely to emerge. Sodium hexametaphosphate is likely to remain an important additive in the paint industry, with its role evolving and expanding in response to technological advancements and changing market demands.
Expand reading:
Sodium hexametaphosphate in toothpaste VS. other phosphates,etc.

