I. Understanding the Importance of Dental Care for Kids
A. Children are prone to dental caries.
- The enamel of children’s milk teeth has a lower degree of mineralization than that of permanent teeth, so it is easy to be eroded by acid, and the enamel is demineralized to form dental caries.
- Children’s oral hygiene habits are poor, many children do not brush their teeth seriously, so that food debris accumulates in the mouth, and it is easy to suffer from dental caries over time.
- Children like to eat sweets, eat more sugar, and sugar is divided into the oral cavity bacteria provide a large number of nutrients, so it is easy to suffer from dental caries.

B. The bad effect of dental caries to kids.
- Proper dental care is of utmost importance for children’s overall health and development. Dental health also has a significant impact on a child’s self-esteem.
- Children with dental problems may experience pain and discomfort, which can affect their mood and behavior.
- Poor dental health can lead to more serious health issues. For example, untreated cavities can lead to infections that may spread to other parts of the body. Research shows that there is a link between oral health and systemic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
II. Introducing Sodium Monofluorophosphate and sodium fluoride
A. Sodium monofluorophosphate for kids
Sodium monofluorophosphate is a chemical compound that is commonly used as an active ingredient in toothpaste. It is a white crystalline powder with a molecular formula of Na2PO3F. This compound has several important physical properties that make it useful in dental care. For example, it is highly soluble in water, which allows it to be easily incorporated into toothpaste formulations.
In terms of its role in toothpaste, sodium monofluorophosphate works by releasing fluoride ions when it comes into contact with saliva. Please check the article “is sodium monofluorophosphate good for your teeth” for it’s detail function for teeth.
As for its sources, sodium monofluorophosphate is typically produced by chemical manufacturers who specialize in the production of dental care products. Our tooth paste sodium monofluorophosphate have been using in big brands tooth paste and protecting kids teeth over two decades.
B. Sodium fluoride for kids
Sodium fluoride, with the chemical formula NaF, is an ionic compound. It has a density of 2.78 g/cm³ and appears as a white powder or colorless crystalline solid. Sodium fluoride is soluble in water and hydrogen fluoride but insoluble in ethanol. The compound is made up of sodium and fluorine elements, with sodium accounting for 54.75% and fluorine for 45.25%..
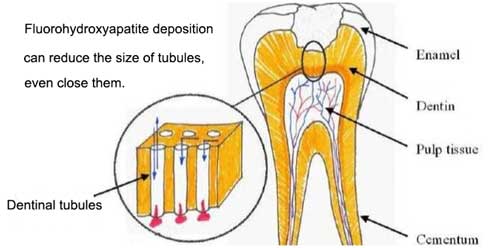
For children, sodium fluoride plays a crucial role in preventing dental caries and strengthening enamel. Toothpaste containing sodium fluoride can be effective in reducing the incidence of cavities. Please check the article sodium fluoride uses for the details.
III. Comparison of the Two for Kids
A. Effectiveness in Preventing Cavities
Both sodium monofluorophosphate and sodium fluoride are effective in preventing cavities in kids. Studies have shown that toothpaste containing either of these substances can significantly reduce the incidence of cavities. Sodium monofluorophosphate works by releasing fluoride ions when it comes into contact with saliva, which then help to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent cavities. Sodium fluoride also releases fluoride ions that combine with hydroxyapatite in tooth enamel to form fluorapatite, which is more resistant to acid attacks.

B. Function differences
Sodium monofluorophosphate has the effect of strengthening teeth and preventing cavities, and it has certain restorative and anti-sensitive function.
Sodium fluoride is mainly used for cavity prevention, its effect is relatively single, no restorative function and anti-sensitive function.
C. Safety Considerations
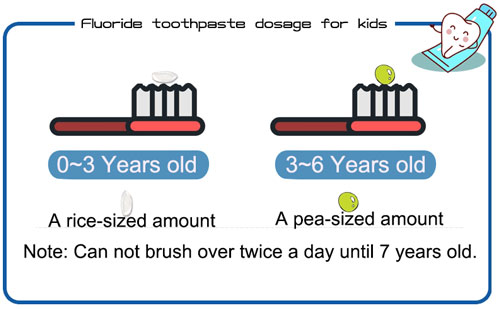
When it comes to safety, both sodium monofluorophosphate and sodium fluoride are generally considered safe for use in children’s dental products. However, it is important to use these products as directed and to avoid overconsumption. Excessive intake of fluoride can lead to fluorosis, a condition characterized by discoloration and pitting of the teeth. Parents should ensure that their children use only a pea-sized amount of toothpaste and that they do not swallow it. Additionally, children under the age of six may need to use a fluoride-free toothpaste or one with a lower concentration of fluoride to reduce the risk of fluorosis.
D. Usage and Application Methods
For kids’ dental care, products containing sodium monofluorophosphate or sodium fluoride can be used in several ways. Toothpaste is the most common product, but mouthwashes and dental rinses may also be available. When using toothpaste, parents should supervise their children to ensure that they use the correct amount and brush properly. It is recommended that children brush their teeth twice a day for two minutes each time when over 7 years old. Mouthwashes and dental rinses should be used according to the instructions on the label. It is important to note that these products are not a substitute for regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Dentists can provide personalized advice on the best products and methods for each child’s dental needs.
IV. Conclusion
When comparing the two for kids, both are effective in preventing cavities, although the effectiveness may vary depending on factors such as concentration, frequency of use, and oral hygiene habits. Regarding safety, both are generally safe when used as directed,.
Sodium monofluorophosphate could reduce tooth sensitivity additionaly, is a valuable ingredient in many toothpaste formulations.
In conclusion, parents and caregivers should be informed about the benefits and considerations of sodium monofluorophosphate and sodium fluoride in dental care products for kids. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings, along with the use of appropriate toothpaste, mouthwashes, and dental rinses, can go a long way in ensuring healthy teeth and a confident smile for children. By making informed choices and promoting good dental habits from an early age, we can set our kids on the path to a lifetime of oral health.