I. Introduction
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaH2PO4·H2O, with the appearance of white crystals or crystalline powder, soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol.
Molecular weight 137.992
CAS No. 10049-21-5
EINECS No. 231-449-2
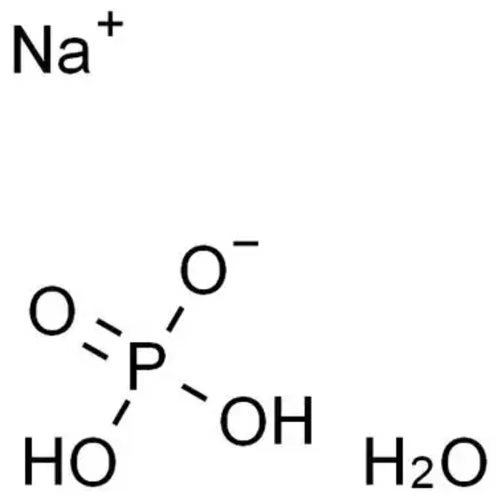
The pH of a solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate usually ranges from 4.5 to 5.5. This pH range is due to the fact that sodium dihydrogen phosphate decomposes into phosphate ions (H2PO4–) and hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution, making its solution acidic. The exact value of the pH is affected by the concentration of the solution and the concentration of the other ions, and the higher the concentration, the lower the pH is likely to be.
II. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate uses
a. Buffer
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate buffer is able to maintain the pH stability of the solution during chemical reactions.
b. Food additives
Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Monohydrate can be used as a thickener, bulking agent and buffer, which is widely used in the manufacturing process of food products such as condiments, canned food, bread and desserts.

c. Pharmaceutical industry
- Prevention and treatment of hypophosphatemia: as a phosphorus additive in total intravenous hypernourishment therapy to prevent hypophosphatemia.
- Adjuvant treatment of urinary tract infections: enhances antibacterial activity by acidifying the urine and eliminates odor and turbidity in urinary tract infections.
- Prevention of Calcium-Containing Kidney Stones: Prevents recurrence of kidney stones by acidifying the urine and increasing the solubility of calcium.
- Other medical uses: including treatment of diarrhea, prevention of acidosis, correction of electrolyte imbalance, relief of angina and improvement of anemia.
III. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate vs Sodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous substance
a. Chemical formula
Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Monohydrate (NaH2PO4-H2O) and Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate (NaH2PO4) are two different compounds that have different molecular and chemical formulas. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate compound is composed of a phosphate ion, two hydrogen ions and a water molecule, while sodium dihydrogen phosphate is composed of a phosphate ion and two hydrogen ions.
b. Stability
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (NaH2PO4-H2O) has good stability at room temperature and is not easy to decompose or deliquesce. At high temperatures or under special conditions, such as when heated to 200°C, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate may decompose.
The chemical properties of anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate are very active and extremely unstable. It reacts easily with acids to form salts and water, can form insoluble complexes or chelates with many metal ions, and can react with strong alkali solutions in a complex decomposition reaction and release hydrogen gas. Anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate can slowly absorb water in the air and gradually form hexahydrate.
c. Medical Applications
Both sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate compound and anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate have important applications in the medical field. Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Monohydrate Compound is a commonly used medication for the treatment of diseases such as liver disease, kidney disease and acidosis. It improves the patient’s symptoms by regulating the acid-base balance in the body. Anhydrous sodium dihydrogen phosphate, on the other hand, is commonly used to prepare buffers for use in biochemistry experiments.
d. Chemistry Experiments
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate also have different applications in chemistry experiments. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate is commonly used to prepare pH 4.8 buffers for DNA purification and PCR amplification. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer is commonly used to be pH 7.0 for protein purification and enzyme reactions.
IV. Conclusion
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate is an anhydrous compound that has a wide range of uses in chemical reactions, food processing, and medicinal applications. It is used interchangeably with sodium dihydrogen phosphate in many ways, but it differs significantly from sodium dihydrogen phosphate anhydrous in chemical formula, stability, and in medical applications and chemical experiments.
Expand reading:
Breif introduction to Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate.

