I.Introduction to the Two Compounds
Sodium monofluorophosphate and sodium lauryl sulfate are two important compounds with significant roles in different industries. Sodium monofluorophosphate is widely known for its applications in toothpaste and other areas, while sodium lauryl sulfate is a common surfactant found in many personal care products.
A. Sodium Monofluorophosphate: An Active Ingredient in Toothpaste
Sodium monofluorophosphate plays a crucial role as an active ingredient in toothpaste. It helps in cavity protection by strengthening the enamel. Research shows that its presence in toothpaste can significantly reduce the risk of cavities. Additionally, it also contributes to cleaning the teeth. With a purity often around 98% as mentioned by some sources, it is a reliable choice for dental care products.
B. Sodium Lauryl Sulfate: A Common Surfactant
Sodium lauryl sulfate is a widely used surfactant in personal care products such as shampoos and toothpastes. It is known for its ability to create foam, giving a rich lathering experience. For example, in shampoos, it helps in removing dirt and oil from the hair. However, it also has some concerns. Studies have shown that it can be irritating to the skin and scalp, especially for those with sensitive skin. The debate over its safety continues, but it is clear that people with sensitive skin should be cautious when using products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
II.Properties and Characteristics
A.Physical and Chemical Properties
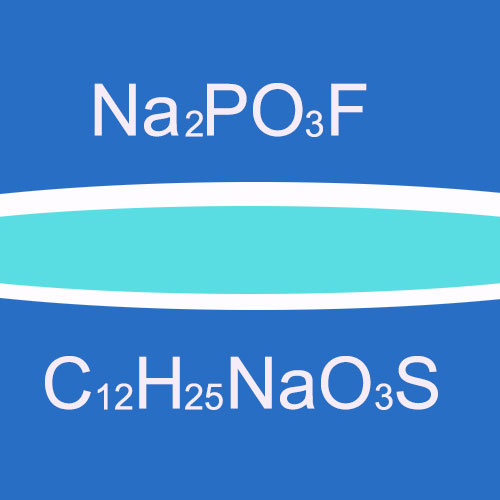
Sodium Monofluorophosphate: Sodium monofluorophosphate is a white powder with a melting point of about 626°C. It is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of 42% at 25°C. It has strong hygroscopicity. The chemical formula is Na2PO3F and the molecular weight is about 144. It has a pH value of 6.5 – 8.0 in a 2% aqueous solution.

Sodium Lauryl Sulfate: Sodium lauryl sulfate is a white or light yellow crystalline or powder. It is easily soluble in hot water and hot ethanol but insoluble in cold water and petroleum ether. The chemical formula is C12H25NaO3S. It is an anionic surfactant with a complex chemical structure.

B.Functional Characteristics
Sodium Monofluorophosphate: In toothpaste, it helps protect against cavities by strengthening tooth enamel. It is also used in other applications such as concrete corrosion inhibitors. In food and medical industries, it can play certain roles although specific applications may vary.
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate: As a surfactant, it is widely used in personal care products like shampoos and toothpastes for its foaming ability. In the chemical and light industry, it serves as an emulsifier, flotation agent, and penetrant. However, its potential to irritate the skin and eyes is a concern, especially for those with sensitive skin. Different concentrations of sodium lauryl sulfate are available in the market, ranging from 40% to 70%, with varying prices.
III. Applications and Uses
A.Sodium Monofluorophosphate in Toothpaste Industry
Sodium monofluorophosphate is a key ingredient in the toothpaste industry. It plays a crucial role in preventing cavities by strengthening the enamel of teeth. When used in toothpaste, it reacts with saliva to release fluoride ions, which are then absorbed by the enamel. This helps to remineralize and strengthen the enamel, making it more resistant to acid attacks from bacteria and food. Research has shown that toothpaste containing sodium monofluorophosphate can reduce the incidence of cavities by up to 40%. In addition to its cavity-preventive properties, sodium monofluorophosphate also helps to clean teeth by removing stains and plaque. It works in conjunction with other ingredients in toothpaste to provide a comprehensive cleaning and protection for teeth.
B.Sodium Lauryl Sulfate in Personal Care and Industrial Products
Sodium lauryl sulfate is widely used in personal care products such as shampoos, toothpastes, and body washes.

- In shampoos, it helps to remove dirt, oil, and styling products from the hair by creating a rich lather.
- In toothpastes, it provides a foaming action that helps to clean teeth and remove debris. However, as mentioned earlier, it can be irritating to the skin and eyes, especially for those with sensitive skin.
- In industrial products, sodium lauryl sulfate is used as an emulsifier, flotation agent, and penetrant. For example, in the detergent industry, it helps to break down dirt and stains and keep them suspended in water so they can be easily rinsed away.
- In the textile industry, it is used as a wetting agent and penetrant to help dyes and finishes adhere to fabrics.
- In the paper industry, it is used as a deinking agent to remove ink from recycled paper. Despite its wide range of applications, the potential risks associated with sodium lauryl sulfate have led to an increased demand for alternative surfactants in personal care products.
IV.Side Effects and Risks
A.Potential Side Effects of Sodium Monofluorophosphate
Although sodium monofluorophosphate is widely used in toothpaste and has significant cavity-preventive benefits, it may have some potential side effects. Some individuals may experience mild tooth sensitivity after using toothpaste containing sodium monofluorophosphate. This could be due to the interaction of the fluoride ions with the tooth enamel. However, such sensitivity is usually temporary and subsides over time. In rare cases, excessive consumption of fluoride-containing products, including those with sodium monofluorophosphate, can lead to fluorosis. Fluorosis can cause discoloration and pitting of the teeth. It is important to use toothpaste with sodium monofluorophosphate in moderation and follow proper dental hygiene practices. (Please check article “Is sodium monofluorophosphate harmful?” for details.)
B.Risks of Sodium Lauryl Sulfate

Sodium lauryl sulfate poses several risks and potential irritations. When it comes to the skin, it can cause dryness, redness, and itching. People with sensitive skin are particularly vulnerable to these effects. In some cases, prolonged use of products containing sodium lauryl sulfate can lead to dermatitis. The eyes are also at risk from sodium lauryl sulfate. Contact with products containing this surfactant can cause irritation, redness, and watering of the eyes. In severe cases, it may even lead to corneal damage. Regarding the respiratory system, inhalation of sodium lauryl sulfate dust can cause irritation and coughing. Workers in industries where sodium lauryl sulfate is used may be at a higher risk of respiratory problems. Additionally, some studies have suggested that sodium lauryl sulfate may disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function, making it more susceptible to other irritants and allergens. This can lead to a cycle of skin problems and further irritation. It is crucial for consumers to be aware of the potential risks associated with sodium lauryl sulfate and make informed choices when selecting personal care products.
V. Conclusion
Sodium monofluorophosphate and sodium lauryl sulfate are two distinct compounds with their own sets of characteristics and applications.
Similarities: Both compounds play important roles in specific industries. Sodium monofluorophosphate is crucial in the toothpaste industry for cavity prevention and cleaning teeth, while sodium lauryl sulfate is widely used in personal care and industrial products as a surfactant for its foaming and cleansing properties.
Differences: In terms of properties, sodium monofluorophosphate is a white powder with a melting point of about 626°C, highly soluble in water, and has a pH value of 6.5 – 8.0 in a 2% aqueous solution. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a white or light yellow crystalline or powder, easily soluble in hot water and hot ethanol but insoluble in cold water and petroleum ether. Sodium monofluorophosphate is mainly used in toothpaste and some industrial applications related to corrosion inhibition, while sodium lauryl sulfate is used as an emulsifier, flotation agent, and penetrant in various industries.
In terms of side effects and risks, sodium monofluorophosphate may cause mild tooth sensitivity and in rare cases, fluorosis. Sodium lauryl sulfate can cause skin dryness, redness, itching, and dermatitis, eye irritation, and may disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function. It can also pose respiratory risks when inhaled.
Both compounds are of great importance in their respective fields. Sodium monofluorophosphate is essential for dental care, helping to protect teeth from cavities and maintain oral health. Sodium lauryl sulfate, despite its potential risks, is widely used in personal care and industrial products due to its functional characteristics as a surfactant. However, consumers should be aware of the potential risks associated with these compounds and make informed choices when using products containing them.
Similar contrasts:
Sodium monofluorophosphate vs zinc sulphate
Sodium monofluorophosphate vs stannous fluoride