Trisodium phosphate is usually safe for humans, but can cause adverse effects in cases of excessive intake.
I. Introduction to trisodium phosphate
Sodium phosphate is a chemical substance, a phosphate, which is susceptible to moisture and weathering in dry air to produce sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium bicarbonate.
Trisodium phosphate is a common food additive and cleaning agent ingredient used to regulate pH and soften water. It is also used as a pharmaceutical ingredient in glucocorticoid drugs. In food, the amount of trisodium phosphate used is strictly regulated to ensure its safety. In the medical field, trisodium phosphate is used in the preparation of certain medications such as trisodium phosphate solutions, trisodium phosphate tablets and trisodium phosphate injections. In daily life and industry, trisodium phosphate cleaner is also an important detergent. It is safe for humans when used in moderate amounts, but excessive intake may cause health problems.

II. Safety information for trisodium phosphate
A.Safety terminology
- S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes。
- S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
- S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
- S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.)
B. Risk terminology
- R34:Causes burns.。
- R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
III. Toxicity of trisodium phosphate
Trisodium phosphate is toxic, especially to humans and the environment.
A. Toxicity to humans
- Skin contact: Trisodium phosphate may cause irritation of the mucous membranes of the skin and discomfort on contact.
- Eye exposure: Trisodium phosphate in the eye can cause chemical burns to the surface of the eye and cornea, causing stinging, redness and swelling, leading to blurred vision. In severe cases, it may even lead to vision loss or loss of vision. It may also cause other complications such as keratitis and conjunctivitis if not treated promptly or properly.
- Inhalation: Inhalation of trisodium phosphate dust or gas may cause respiratory tract irritation, resulting in coughing, dyspnea, and can be fatal due to spasm, inflammation, and edema of the larynx and bronchial tubes, chemical pneumonitis, or pulmonary edema. In case of inadvertent inhalation, move away from the source of contamination as soon as possible and call for first aid.
- Ingestion: Ingestion of large amounts of trisodium phosphate may cause gastrointestinal irritation leading to vomiting and abdominal pain. If ingested in large quantities over a long period of time, it may interfere with calcium absorption and lead to osteoporosis.
B. Toxicity to the environment
Excessive discharges of trisodium phosphate can lead to elevated phosphorus concentrations in water bodies, affecting aquatic organisms and possibly leading to deterioration of water quality. In addition, if a large amount of trisodium phosphate enters the soil, it may also affect the ecology of the soil.
IV. Safe use of trisodium phosphate

- In detergents, a concentration of 5-10% is usually recommended;
- In food processing, when used as an emulsifier and stabilizer, the amount added should not exceed 2% of the total amount of food. For example, in cheese, the maximum use level is 5g/kg; in ham, meat, fish, shrimp and crab, the maximum use level is 3.0g/kg; in canned food, fruit juice, beverage and dairy products, the maximum use level is 0.5g/kg.
- In water treatment, as a water softener, its dosage needs to be adjusted according to the water hardness, generally adding 10-50 mg per liter of water.
These ratios are for reference only, and should be adjusted according to the actual situation and relevant regulations for specific use. For example, to know how much trisodium phosphate is in cereal, we need to check the ingredient list of the cereal and make sure it is manufactured by legitimate manufacturer.
V. Emergency measures for inadvertent overexposure
A. Inadvertent Contact
Remove contaminated clothing and immediately rinse thoroughly with plenty of running water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
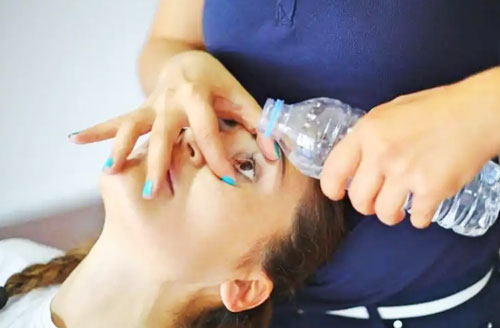
B. Inadvertent eye contact
In the event that trisodium phosphate enters the eye, immediately roll open the upper and lower eyelids and flush with running water or saline for at least 15 minutes. And seek medical attention as soon as possible. During flushing, be careful to roll the eyelids and turn the eye up and down, but avoid flushing directly into the dark eyeball. After flushing, if there is only mild stinging and redness in the eye, antibiotic drops can be used to prevent infection. And you should go to the ophthalmology department in time.
C. Accidental ingestion
- Rinse mouth immediately.
- Drink milk or egg white.
- Drink plenty of water to dilute the concentration of sodium phosphate in the body and facilitate its elimination.
- Seek medical help. Perform gastric lavage, induce vomiting and other treatments under medical supervision.
D. Inhalation
Get out of the scene quickly to fresh air. Keep airway open. Give oxygen if breathing is difficult. If breathing stops, give artificial respiration immediately. Seek medical attention.
VI. How to handle trisodium phosphate safely

- When using and handling during trisodium phosphate manufacturing process, a series of safety measures must be taken to protect the safety of humans and the environment.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, eyeglasses and masks.
- Ensure that the operating area is well ventilated to avoid inhalation or exposure to large quantities of trisodium phosphate.
- Follow proper operating procedures and safety practices when handling trisodium phosphate.
- After used, proper trisodium phosphate disposal is necessary for the remaining material and avoid releasing it into the environment.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, trisodium phosphate is a commonly used food additive, water softener, and chemical additive. It is safe for humans when used in moderate amounts. However, excessive exposure or ingestion may cause health problems. It can cause skin irritation, eye damage, respiratory irritation and other symptoms. There may be some risk to humans and the environment. After inadvertent overexposure, take immediate emergency measures and seek medical attention immediately. When using and handling trisodium phosphate, it is important to strictly observe safe operating practices, take appropriate personal protective measures, and properly dispose of the remaining substance to protect human health and environmental safety.
Related article:

